#9 Eyes: (This particular lecture is much longer when I teach. This is just scratching the surface regarding eye animation.)
Basic Notes on animating Eyes:
- Eyes are windows into the soul and the soul is controlled by the mind.
- Eye darts and glances tell more than any other gestures in the body when used in the right place in the scene.
- Desire is always described in the eyes, even when hidden through subtext acting choices.
- Never animate without a reason!
- Force vs. Form
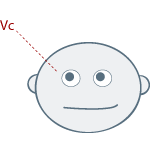
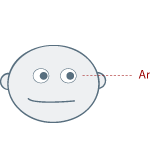
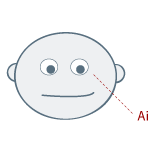
- Look for patterns in the eye darts = Social Triangle – Right Eye, Left Eye and then mouth.
Watch the eye darts as Charlize Theron plays Aileen Wuornos in the movie Monster. They describe her insecurity, her uneasiness and fear that someone might overhear her conversation, not mention the fact she is lying.
- No more than 1-2 frames then hold it to register what char is looking at. If there is any ease, it happens at the end of the dart.
- Linear Curves, I only put eases on slower eye motion. I tend to sculpt motion with tangents. If you prefer to set a lot of keys to create your motion, then I would advise putting eases into your eye darts with your keys.
- Dart then stay -and dart then stay, if you do not stay in one place the eye dart will never read. You can use two eye darts to move the eye a far way, so it still reads as an eye dart. Otherwise it’s just a look.
- Triangle Motion: left eye, right eye, mouth. This is the basic motion most eye darts take when conversing. Even when the other person is not speaking we tend to look back and forth in this triangular motion to read the other person’s face.
- Be careful with how far you tilt the yes on the social triangle for eye darts or it will move into an intimate gaze zone. When people approach each other from a distance, they look quickly between the other person's face and lower body to first establish what the sex of the person is and then a second time to determine a level of interest in them. This gaze is across the eyes and below the chin to lower parts of the person's body. In close encounters, it's the triangular area between the eyes and the chest and for distant gazing it's from the eyes to the crotch or below.
- Also be careful to not raise the darts higher than the brow line. Then, you are entering the power gaze zone. Provided your gaze doesn't drop below the level of their eyes, the pressure will stay on the person being gazed upon. Never use this in friendly or romantic encounters. It works well for intimidation.
- When to use eye darts? Thought process… shows thinking. Stress, Assessing. Moving holds are when they read best. When your character has stopped moving so much and you can read them.
- Eye Darts and the head and neck. Nothing in the body is ever still. Occasionally the head will make a slight movement after the eye darts one way or another. Very slight though. Have you ever ridden a motorcycle? The bike will go where you are looking naturally, so do not look at the curb! Same thing goes for your head and the eyes.
- On most character designs the upper lid covers most of the eye and the lower lid, barely moves to reach. The blink line is usually ¾ down on the eye, not in the middle. The closed position is actually an overshoot of the upper lid pushing on the lower lid.
- Everything I just said above can be affected / changed by emotional cures, lid shapes and other triggers.
- Lots of blinking shows insecurity, bumbling, nervous and confused. A direct stare is connected to emotions like fight or love. Check out the movie I uploaded to the social group on Michael Caine. Fear = no blinking.
- Length of blinks. Get inside the head of your character… if they are sleepy the closed position would be longer than a “zoinks!” WTF kind of blink. Slow blinks can be triggered by sadness, boredom or sleepiness or drugged. Half Blink and twitches again show uncertainty in what the character is seeing or hearing.
- On average it takes more frames to open the eye than close it due to momentum. Ease out to open, but less to no ease on a closed eye.
- Offset shapes in eyes to create more natural motion and then the actual closed point should be on the same frame and then eases are offset again as they reopen. I think the Pixar blink can feel sleepy.
- Move the eye line on a blink when the eye direction changes, if you don’t it will look weird.
- Double take usually involves all of the blinks = full, half and twitchy blinks. Check out the double take example I uploaded to the social group.
- Shape the lid to compliment the brow shapes… angles up and down create added emotion. A blink that arcs down is more elegant looking. A blink that arcs up usually works with a squint and is related to happy blinks.
- Squints tend to happen on “T’s”, “S’s” and “P’s
- An antic like a squint before blinking can help slower blinks or create emotional cues of a change in emotion during the blink.
- If you have an extreme close up, you can adjust pupil size too. Dilate = pleasure. If you are excited, your pupils can dilate up to four times. Conversely, if you are experiencing anger or another negative emotion, your pupils shrink in size. Dilating pupils are also signal of courtship. Maybe this is the reason why romantic encounters succeed in dimly lit places, because pupils naturally dilate in such light conditions.
- Don’t occlude more than 50% of the pupil. You will look interest and appeal in your poses.
- If the lid covers the eye too much it looks sleepy or drugged. A soft eye solution will have to be countered many times depending on the angle of the head and the camera.
- What is the color of your front door?
- What will you look like in 15 years?
- What does your favorite music sound like?
- What would your voice sound like if you had marbles in your mouth?
- When you talk to yourself, what type of voice do you use?
- What does it feel like to be in a nice warm bath?
Note: The above eye patterns are how your eyes would move if you are right-handed. The following picture describes the eye patterns for a right-handed person as you look at them - please note this distinction. These patterns are fairly consistent across all races, with the possible exception of the Basques, who appear to have a number of exceptions to the rule. For many left-handed people, the chart is reversed i.e. mirror image.